Security Group
1. Overview
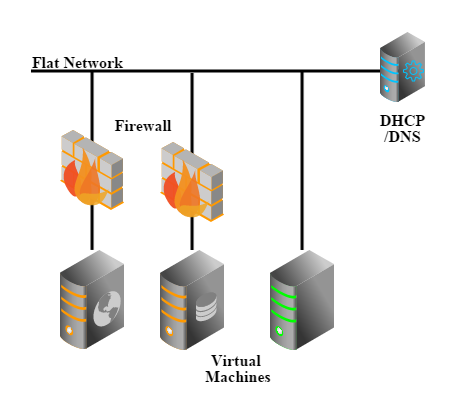
Security group is a virtual firewall that can control the traffic for a group of VMs. In this example, we will create a flat network with a security group, then create one VM(INNER-VM) in the security group and another VM(OUTER-VM) out of the security group. The security group will initially contain a rule opening port 22 to the OUTER-VM; we will confirm OUTER-VM can SSH login the INNER-VM; later on, we will remove the only rule and confirm OUTER-VM cannot SSH login INNER-VM anymore.
2. Prerequisites
We assume you have followed Quick Installation Guide to install ZStack on a single Linux machine, and the ZStack management node is up and running. To use the command line tool, type below command in your shell terminal:
#zstack-cli
Connect to a remote management node
By default, zstack-cli connects to the ZStack management node on the local machine. To connect to a remote node, using option '-H ZSTACK_NODE_HOST_IP'; for example: zstack-cli -H 192.168.0.224To make things simple, we assume you have only one Linux machine with one network card that can access the internet; besides, there are some other requirements:
- At least 20G free disk that can be used as primary storage and backup storage
- Several free IPs that can access the internet
- NFS server is enabled on the machine (done in Quick Installation Guide)
- SSH credentials for user root (done in Quick Installation Guide)
Configure root user
The KVM host will need root user credentials of SSH, to allow Ansible to install necessary packages and to give the KVM agent full control of the host. As this tutorial use a single machine for both ZStack management node and KVM host, you will need to configure credentials for the root user.CentOS:
sudo su
passwd rootBased on those requirements, we assume below setup information:
- ethernet device names: eth0
- eth0 IP: 172.20.11.34
- free IP range: 10.121.9.40 ~ 10.121.9.200 (these IPs can access the internet)
- primary storage folder: /zstack_ps
- backup storage folder: /zstack_bs
Slow VM stopping due to lack of ACPID:
Though we don't show the example of stopping VM, you may find stopping a VM takes more than 60s. That's because the VM image doesn't support ACPID that receives KVM's shutdown event, ZStack has to wait for 60 seconds timeout then destroy it. It's not a problem for regular Linux distributions which have ACPID installed.Avoid DHCP conflict
Please make sure you don't have a DHCP server in the network because ZStack will spawn its own DHCP server; if you have a DHCP server in the network and cannot remove it, please use an IP range that is unlikely used by your DHCP server, otherwise the VM may not receive an IP from ZStack's DHCP server but from yours.3. LogIn
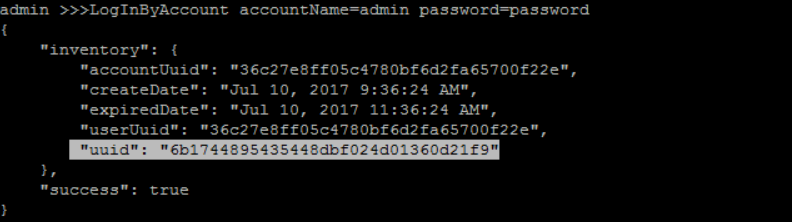
open zstack-cli and login with admin/password:
>>> LogInByAccount accountName=admin password=password
4. Create Zone
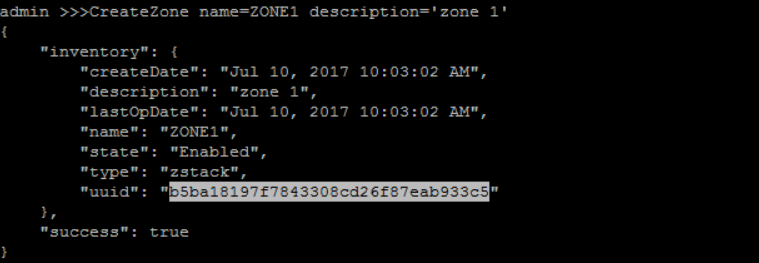
create a zone with name 'ZONE1' and description 'zone 1':
>>> CreateZone name=ZONE1 description='zone 1'
Substitute your UUIDs for those in this tutorial
Resources are all referred by UUIDs in CLI tutorials. The UUIDs are generated by ZStack when you create a resource, so they may vary from what you see in tutorials. UUIDs of resources will be printed out in a JSON object to the screen after resources are created; however, it's inconvenient to scroll up screen to find UUIDs of resources that are created very early. We add buttons to sections, which will show you commands of retrieving UUIDs of resources,
so please make sure you replace UUIDs in tutorials with yours.
to sections, which will show you commands of retrieving UUIDs of resources,
so please make sure you replace UUIDs in tutorials with yours.
5. Create Cluster
create a cluster with name 'CLUSTER1' and hypervisorType 'KVM' under zone 'ZONE1':
QueryZone fields=uuid, name=ZONE1>>> CreateCluster name=CLUSTER1 hypervisorType=KVM zoneUuid=b5ba18197f7843308cd26f87eab933c5
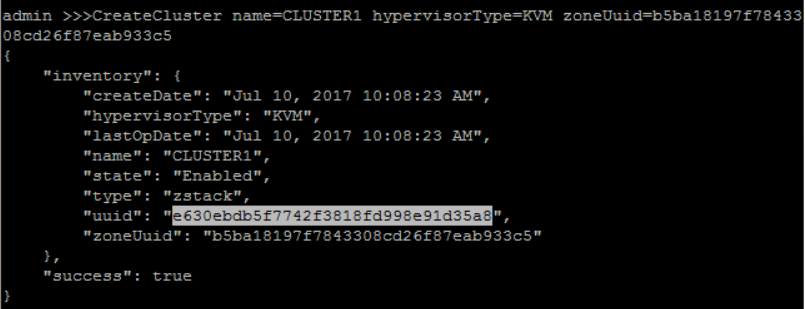
6. Create Host
add KVM Host 'HOST1' under 'CLUSTER1' with correct host IP address and root username and password:
QueryCluster fields=uuid, name=CLUSTER1>>> AddKVMHost name=HOST1 managementIp=172.20.11.34 username=root password=password clusterUuid=e630ebdb5f7742f3818fd998e91d35a8
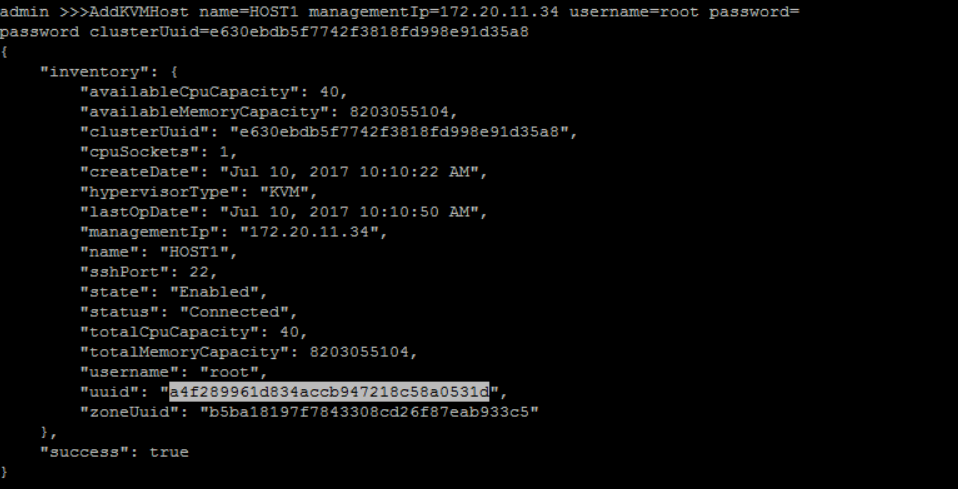
A little slow when first time adding a host
It may take a few minutes to add a host because Ansible will install all dependent packages, for example, KVM, on the host.7. Add Primary Storage
add Primary Storage 'PRIMAYR-STORAGE1' with URL '/zstack_ps' under zone 'ZONE1':
QueryZone fields=uuid, name=ZONE1>>> AddLocalPrimaryStorage name=PRIMARY-STORAGE1 url=/zstack_ps zoneUuid=b5ba18197f7843308cd26f87eab933c5
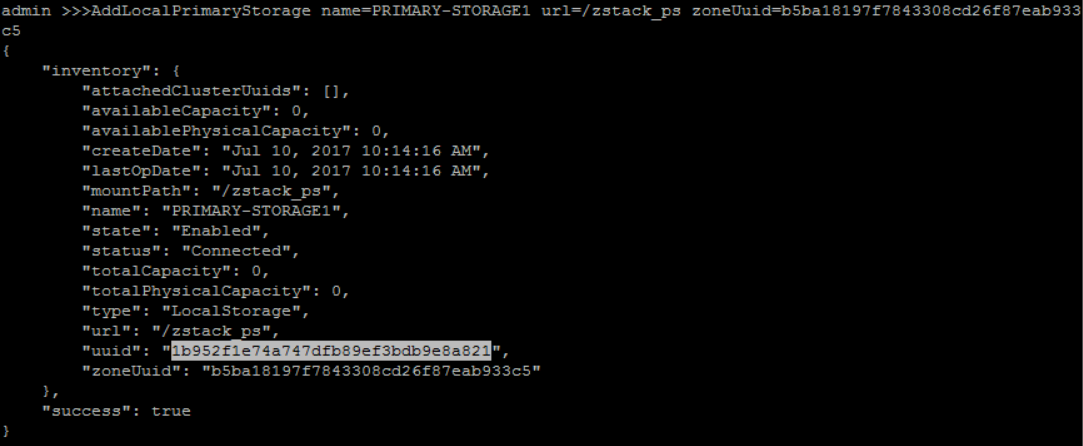
Format of URL
The format of URL is exactly the same to the one used by Linux mount command.attach 'PRIMARY-STORAGE1' to 'CLUSTER1':
QueryCluster fields=uuid, name=CLUSTER1QueryPrimaryStorage fields=uuid, name=PRIMARY-STORAGE1>>> AttachPrimaryStorageToCluster primaryStorageUuid=1b952f1e74a747dfb89ef3bdb9e8a821 clusterUuid=e630ebdb5f7742f3818fd998e91d35a8
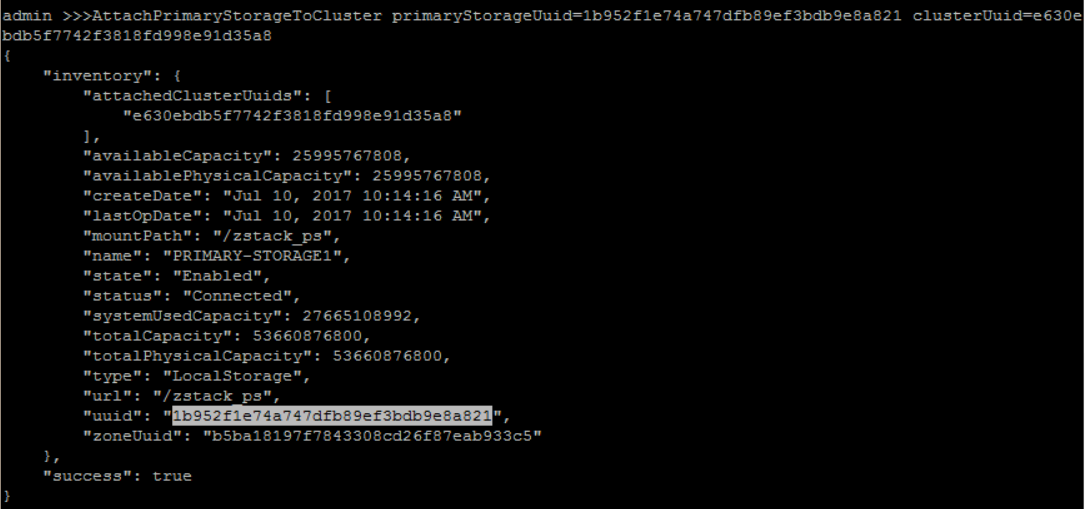
8. Add Backup Storage
add sftp Backup Storage 'BACKUP-STORAGE1' with backup storage host IP address('172.20.11.34'), root username('root'), password('password') and sftp folder path('/zstack_bs'):
>>> AddSftpBackupStorage name=BACKUP-STORAGE1 hostname=172.20.11.34 username=root password=password url=/zstack_bs
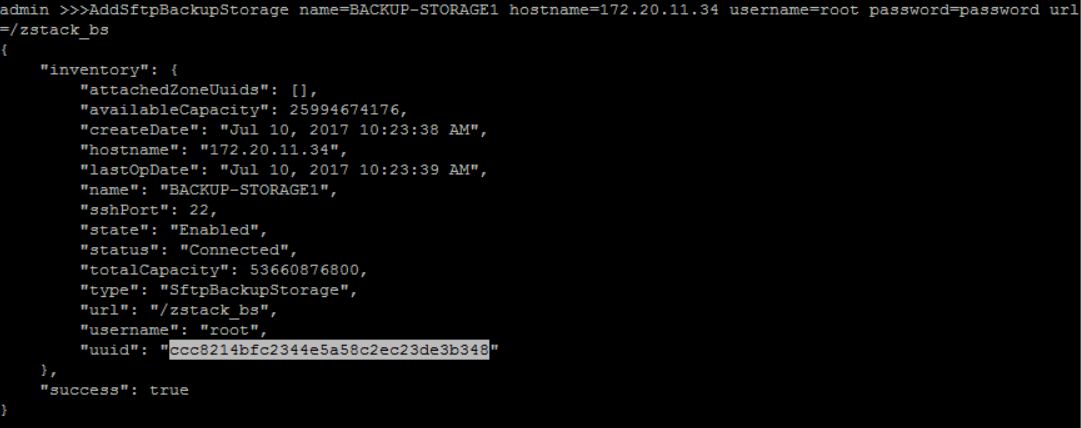
attach new created Backup Storage('BACKUP-STORAGE1') to zone('ZONE1'):
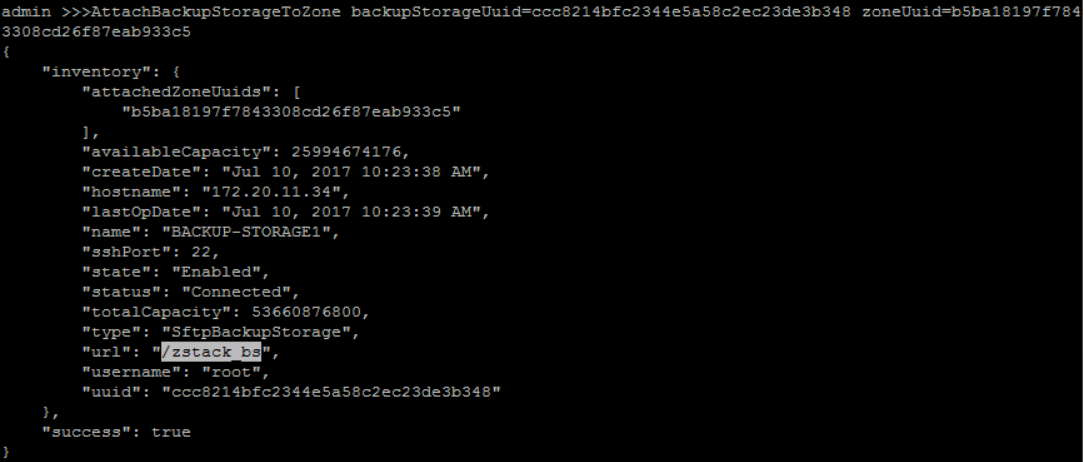
QueryZone fields=uuid, name=ZONE1QueryBackupStorage fields=uuid, name=BACKUP-STORAGE1>>> AttachBackupStorageToZone backupStorageUuid=ccc8214bfc2344e5a58c2ec23de3b348 zoneUuid=b5ba18197f7843308cd26f87eab933c5
9. Add Image
add Image('image') with format 'qcow2', 'RootVolumeTemplate' type, 'Linux' platform and image URL('http://cdn.zstack.io/product_downloads/images/zstack-image.qcow2') to backup storage ('BACKUP-STORAGE1'):
QueryBackupStorage fields=uuid, name=BACKUP-STORAGE1>>> AddImage name=image mediaType=RootVolumeTemplate platform=Linux url=http://192.168.200.100/mirror/diskimages/zstack-image-1.4.qcow2 backupStorageUuids=ccc8214bfc2344e5a58c2ec23de3b348 format=qcow2
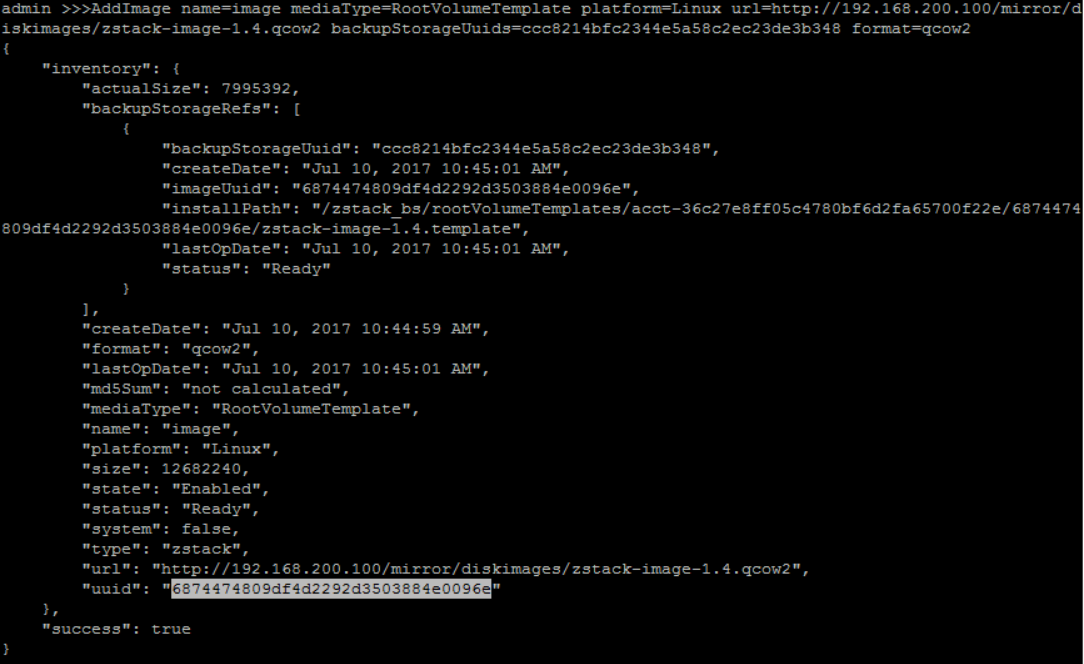
this image will be used as user VM image.
10. Create L2 Network
create No Vlan L2 Network 'PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L2' with physical interface as 'eth0' under 'ZONE1':
QueryZone fields=uuid, name=ZONE1>>> CreateL2NoVlanNetwork name=PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L2 physicalInterface=eth0 zoneUuid=b5ba18197f7843308cd26f87eab933c5
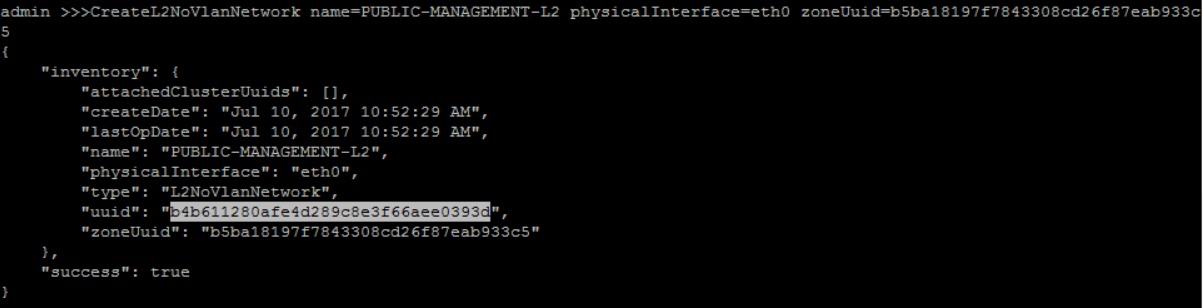
attach 'PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L2' to 'CLUSTER1':
QueryCluster fields=uuid, name=CLUSTER1QueryL2Network fields=uuid, name=PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L2>>> AttachL2NetworkToCluster l2NetworkUuid=b4b611280afe4d289c8e3f66aee0393d clusterUuid=e630ebdb5f7742f3818fd998e91d35a8
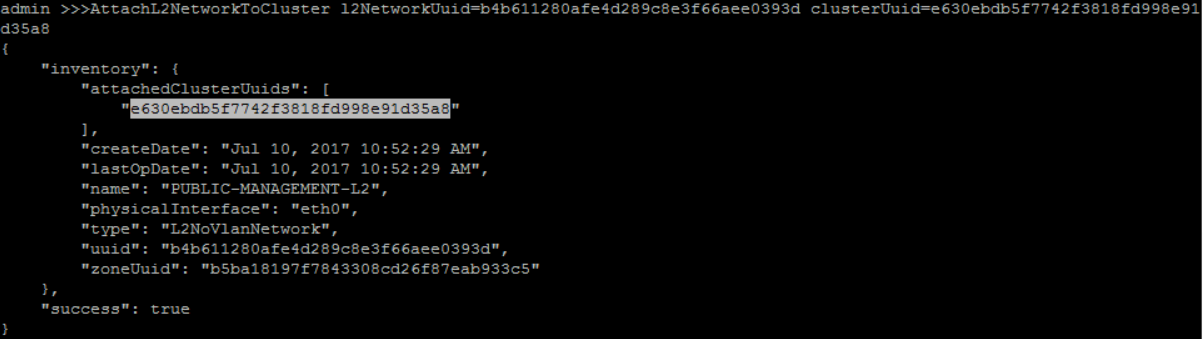
create new private Vlan L2 network 'PRIVATE-L2' with physical interface as 'eth0' and vlan '100' under 'ZONE1':
QueryZone fields=uuid, name=ZONE1>>> CreateL2VlanNetwork name=PRIVATE-L2 physicalInterface=eth0 vlan=100 zoneUuid=b5ba18197f7843308cd26f87eab933c5

attach 'PRIVATE-L2' to 'CLUSTER1':
QueryCluster fields=uuid, name=CLUSTER1QueryL2Network fields=uuid, name=PRIVATE-L2>>> AttachL2NetworkToCluster l2NetworkUuid=b052b4e080c840f6984c29581b167644 clusterUuid=e630ebdb5f7742f3818fd998e91d35a8

11. Create L3 Network
on L2 'PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L2', create a Public Management L3 'PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3' with system set to 'True':
QueryL2Network fields=uuid, name=PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L2>>> CreateL3Network name=PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3 l2NetworkUuid=b4b611280afe4d289c8e3f66aee0393d system=true
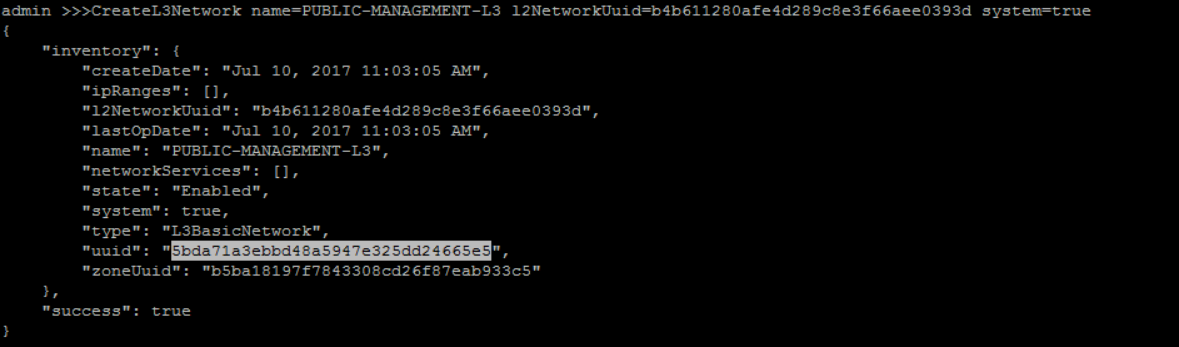
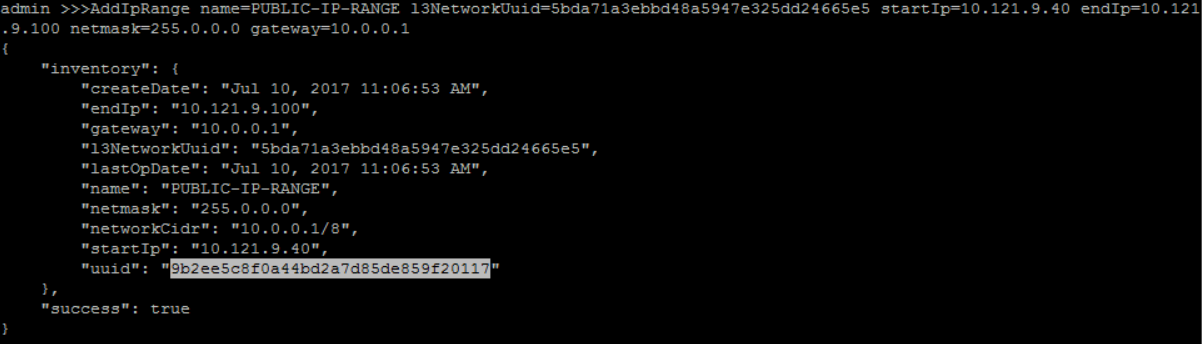
create IP Range for 'PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3':
QueryL3Network fields=uuid, name=PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3>>> AddIpRange name=PUBLIC-IP-RANGE l3NetworkUuid=5bda71a3ebbd48a5947e325dd24665e5 startIp=10.121.9.40 endIp=10.121.9.100 netmask=255.0.0.0 gateway=10.0.0.1
No network services needed for PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3'
No user VMs will be created on the public L3 network in this tutorial, so we don't specify any network services for it.12. Create Router Image
add Image('VRImage') with format 'qcow2' and image URL('http://cdn.zstack.io/product_downloads/images/zstack-image.qcow2') to backup storage ('BACKUP-STORAGE1'):
QueryBackupStorage fields=uuid, name=BACKUP-STORAGE1>>> AddImage name=VRImage url=http://192.168.200.100/mirror/diskimages/zstack-vrouter-latest.qcow2 backupStorageUuids=ccc8214bfc2344e5a58c2ec23de3b348 format=qcow2
Fast link for users of Mainland China
.................................http://cdn.zstack.io/product_downloads/vrouter/zstack-vrouter-2.0.0.qcow2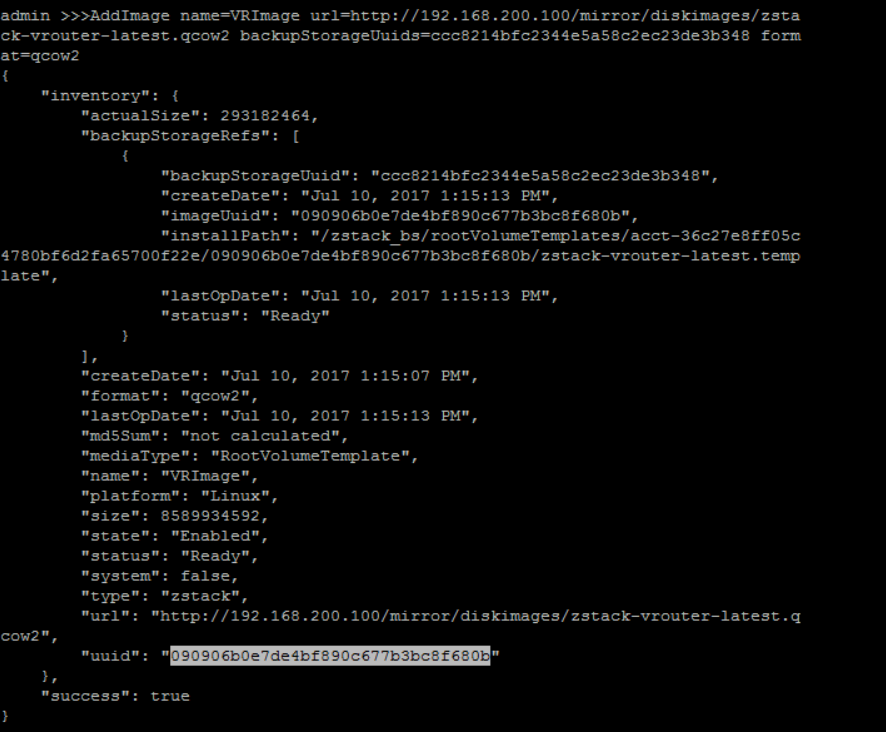
this image will be used as Virtual Router VM image.
Cache images in your local HTTP server
The virtual router image is about 432M that takes a little of time to download. We suggest you use a local HTTP server to storage it and images created by yourself.13. Create Virtual Router Offering
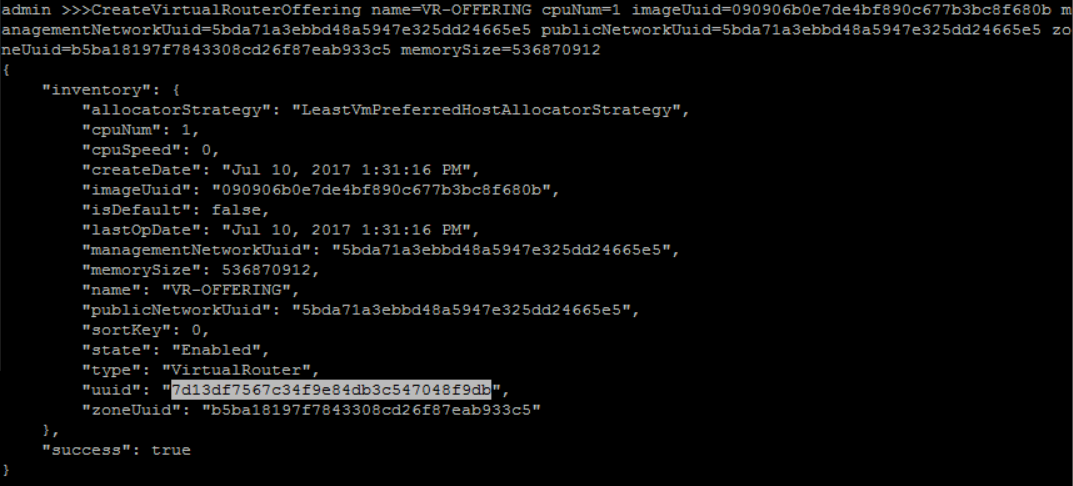
create a Virtual Router VM instance offering 'VR-OFFERING' with 1 CPU, 512MB memory, management L3 network 'PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3', public L3 network 'PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3' and isDefault 'True':
QueryImage fields=uuid, name=VIRTUAL-ROUTERQueryL3Network fields=uuid,name, name?=PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3,PRIVATE-L3QueryZone fields=uuid, name=ZONE1>>> CreateVirtualRouterOffering name=VR-OFFERING cpuNum=1 imageUuid=090906b0e7de4bf890c677b3bc8f680b managementNetworkUuid=5bda71a3ebbd48a5947e325dd24665e5 publicNetworkUuid=5bda71a3ebbd48a5947e325dd24665e5 zoneUuid=b5ba18197f7843308cd26f87eab933c5 memorySize=536870912
14. Create Private Network
on L2 network 'PRIVATE-L2', create a new guest VM L3 'PRIVATE-L3':
QueryL2Network fields=uuid, name=PRIVATE-L2>>> CreateL3Network name=PRIVATE-L3 l2NetworkUuid=b052b4e080c840f6984c29581b167644

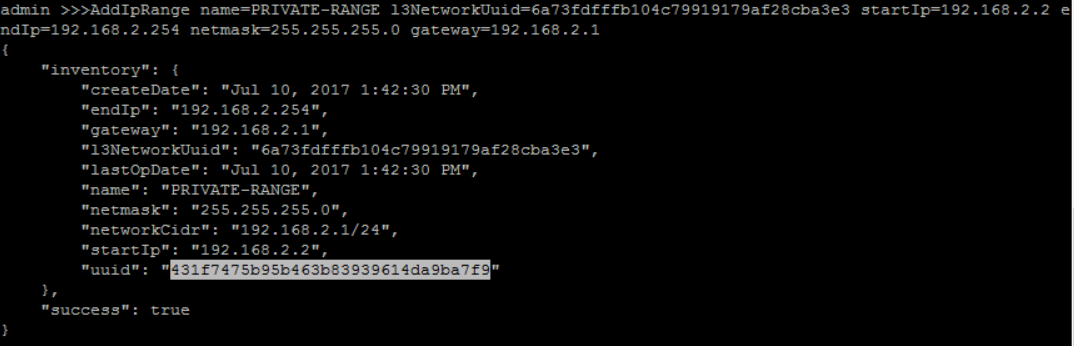
create an IP Range for 'PRIVATE-L3':
QueryL3Network fields=uuid, name=PRIVATE-L3>>>AddIpRange name=PRIVATE-RANGE l3NetworkUuid=6a73fdfffb104c79919179af28cba3e3 startIp=192.168.2.2 endIp=192.168.2.254 netmask=255.255.255.0 gateway=192.168.2.1
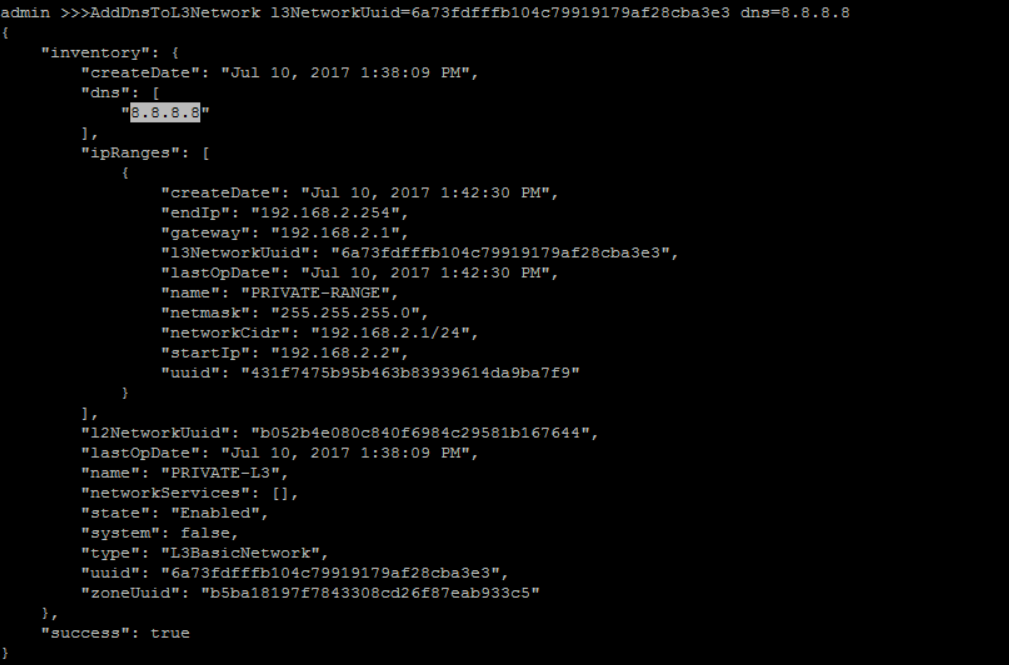
add DNS for 'PRIVATE-L3':
QueryL3Network fields=uuid name=PRIVATE-L3>>> AddDnsToL3Network l3NetworkUuid=6a73fdfffb104c79919179af28cba3e3 dns=8.8.8.8
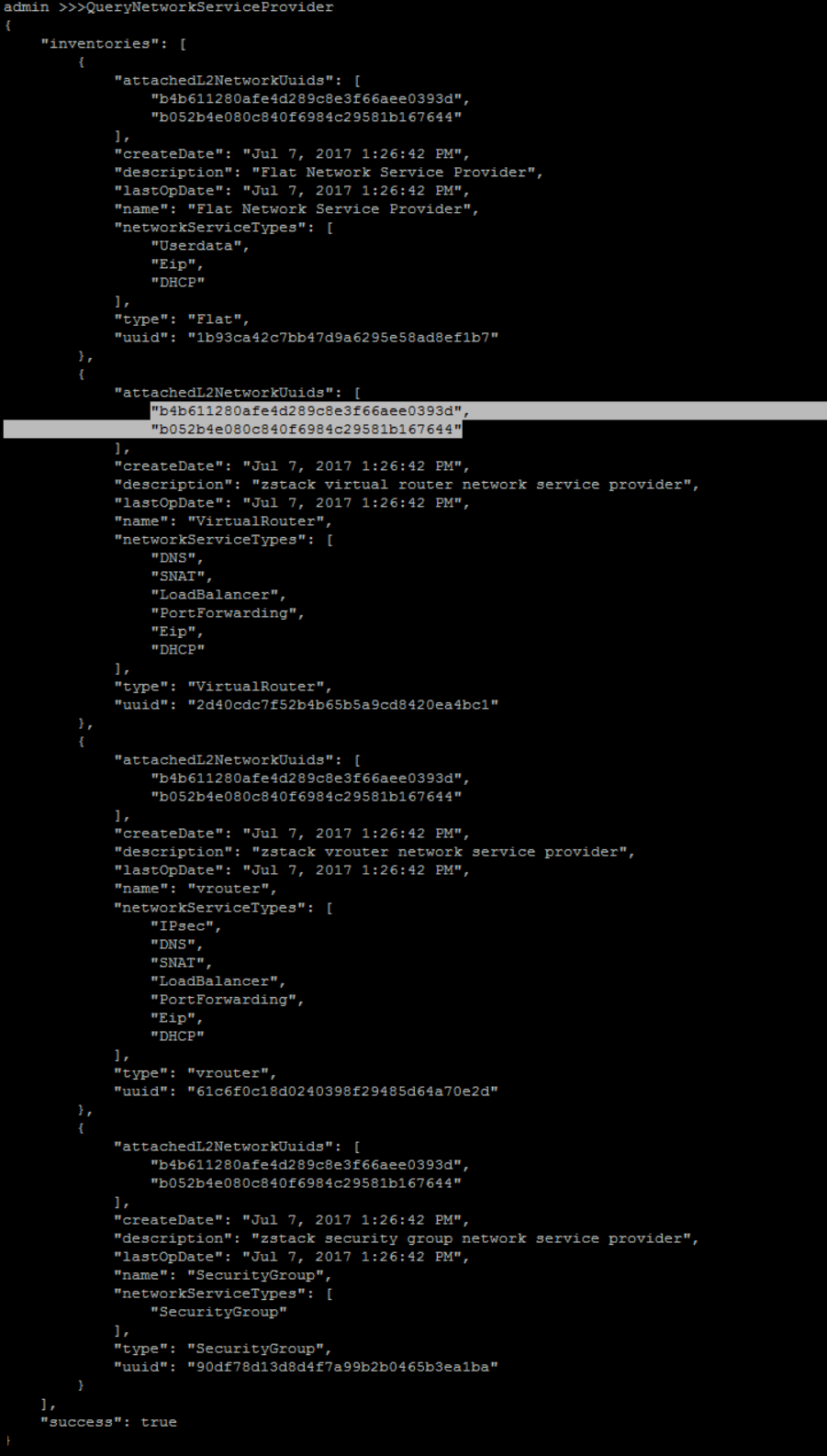
we need to get available network service provider UUID, before add any virtual router service to L3 network:
>>> QueryNetworkServiceProvider
QueryL3Network fields=uuid, name=PRIVATE-L3QueryNetworkServiceProvider fields=uuid, name=VirtualRouterattach SecurityGroup services to 'FLAT-L3':
QueryL3Network fields=uuid, name=FLAT-L3QueryNetworkServiceProvider fields=uuid,name name?=VirtualRouter,SecurityGroupStructure of parameter networkServices
It's a JSON object of map that key is UUID of network service provider and value is a list of network service types.>>> AttachNetworkServiceToL3Network networkServices="{'90df78d13d8d4f7a99b2b0465b3ea1ba':['SecurityGroup']}" l3NetworkUuid=6a73fdfffb104c79919179af28cba3e3
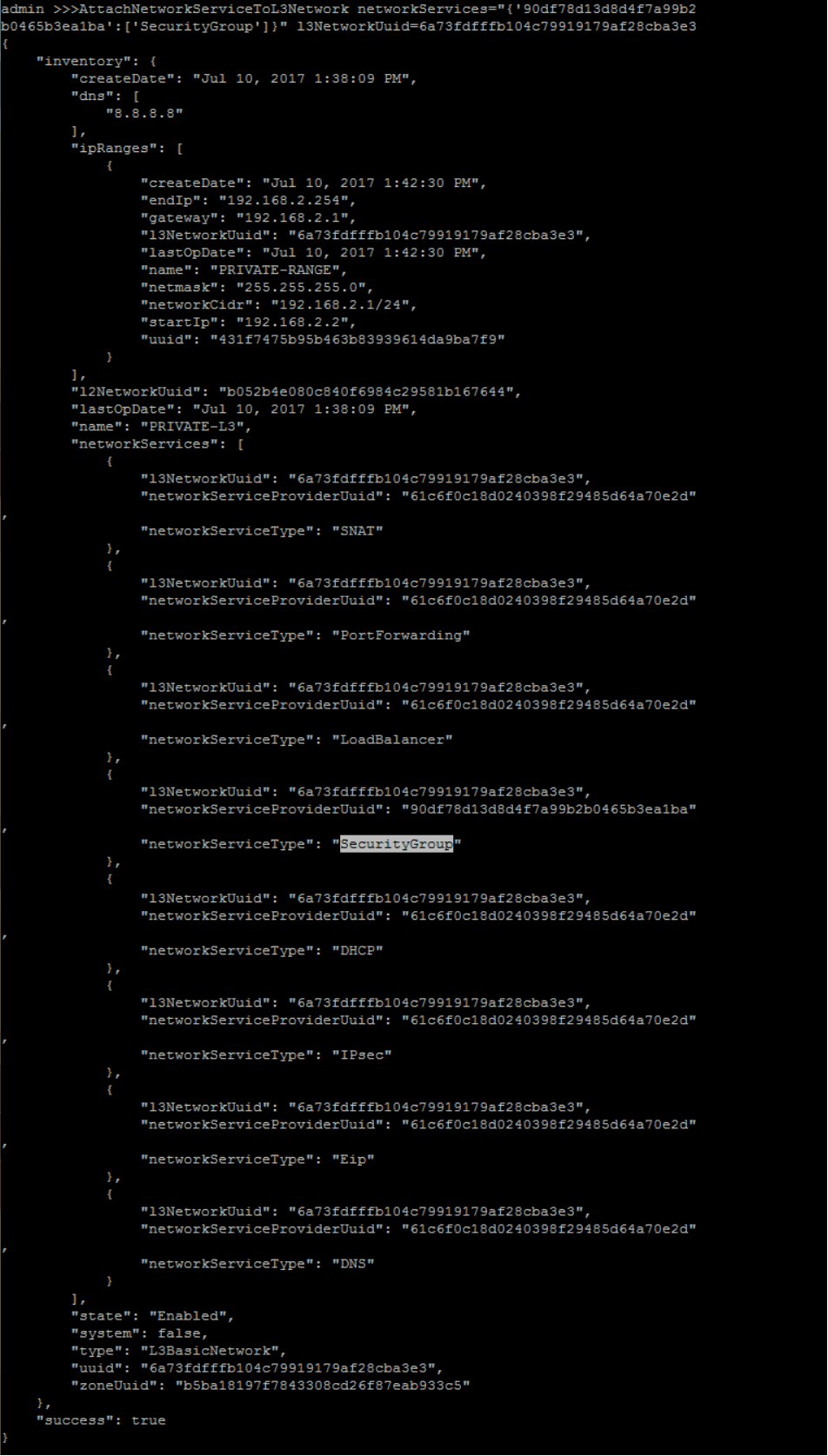
12. Create Security Group
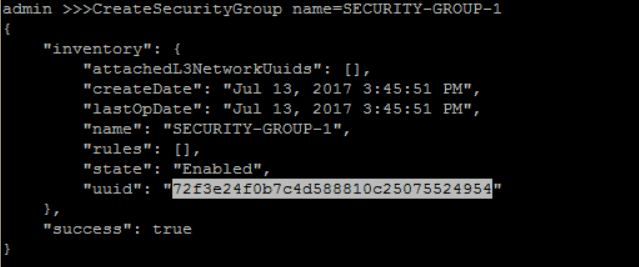
create Security Group 'SECURITY-GROUP-1':
>>> CreateSecurityGroup name=SECURITY-GROUP-1
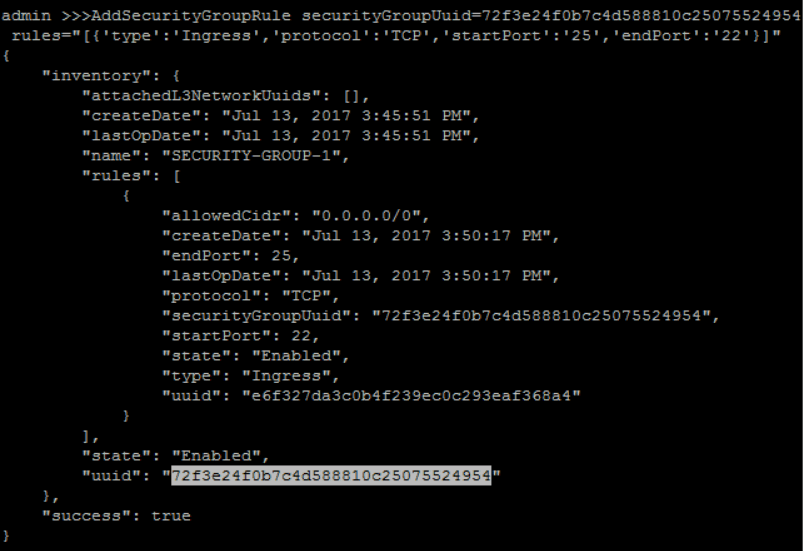
create Security Group Rule for 'SECURITY-GROUP-1':
- type: 'Ingress'
- start port: as 23
- end port: 25
- protocol: 'TCP'
- CIDR: 0.0.0.0/0
QuerySecurityGroup fields=uuid, name=SECURITY-GROUP-1>>> AddSecurityGroupRule securityGroupUuid=72f3e24f0b7c4d588810c25075524954 rules="[{'type':'Ingress','protocol':'TCP','startPort':'25','endPort':'22'}]"
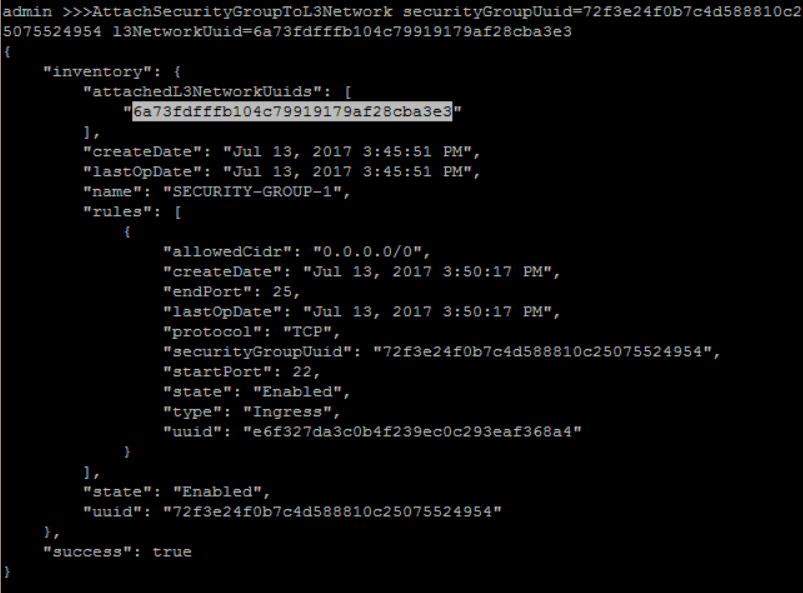
attach 'SECURITY-GROUP-1' to 'PRIVATE-L3':
QuerySecurityGroup fields=uuid, name=SECURITY-GROUP-1QueryL3Network fields=uuid, name=PRIVATE-L3>>> AttachSecurityGroupToL3Network securityGroupUuid=72f3e24f0b7c4d588810c25075524954 l3NetworkUuid=6a73fdfffb104c79919179af28cba3e3
13. Create Instance Offering
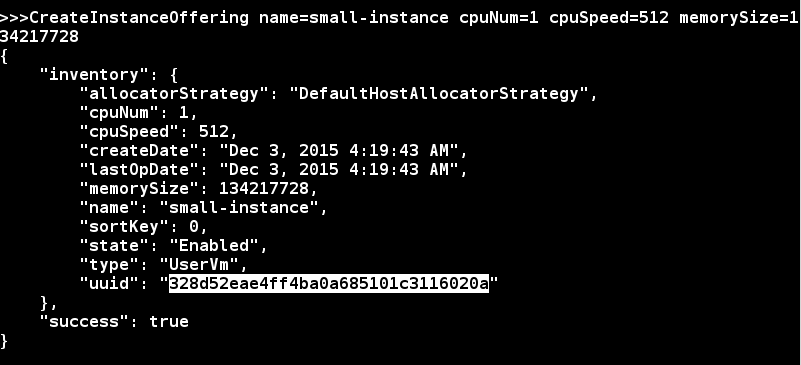
create a guest VM instance offering 'small-instance' with 1 512Mhz CPU and 128MB memory:
>>> CreateInstanceOffering name=small-instance cpuNum=1 cpuSpeed=512 memorySize=134217728
14. Create Virtual Router Offering
create a Virtual Router VM instance offering 'VR-OFFERING' with 1 CPU, 512MB memory, management L3 network 'PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3', public L3 network 'PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3' and isDefault 'True':
QueryImage fields=uuid, name=VIRTUAL-ROUTERQueryL3Network fields=uuid,name, name?=PUBLIC-MANAGEMENT-L3,PRIVATE-L3QueryZone fields=uuid, name=ZONE1>>> CreateVirtualRouterOffering name=VR-OFFERING cpuNum=1 imageUuid=090906b0e7de4bf890c677b3bc8f680b managementNetworkUuid=5bda71a3ebbd48a5947e325dd24665e5 publicNetworkUuid=5bda71a3ebbd48a5947e325dd24665e5 zoneUuid=b5ba18197f7843308cd26f87eab933c5 memorySize=536870912

15. Create INNER-VM
create a new guest VM instance with instance offering 'small-instance', image 'zs-sample-image', L3 network 'PRIVATE-L3', name 'INNER-VM' and hostname 'inner'
QueryInstanceOffering fields=uuid, name=small-instanceQueryImage fields=uuid, name=imageQueryL3Network fields=uuid, name=FLAT-L3>>> CreateVmInstance name=INNER-VM instanceOfferingUuid=025d33f751e241a5b89862e3da2dac47 imageUuid=6874474809df4d2292d3503884e0096e l3NetworkUuids=6a73fdfffb104c79919179af28cba3e3
The first user VM takes more time to create
For the first user VM, ZStack needs to download the image from the backup storage to the primary storage and create a virtual router VM on the private L3 network, so it takes about 1 ~ 2 minutes to finish.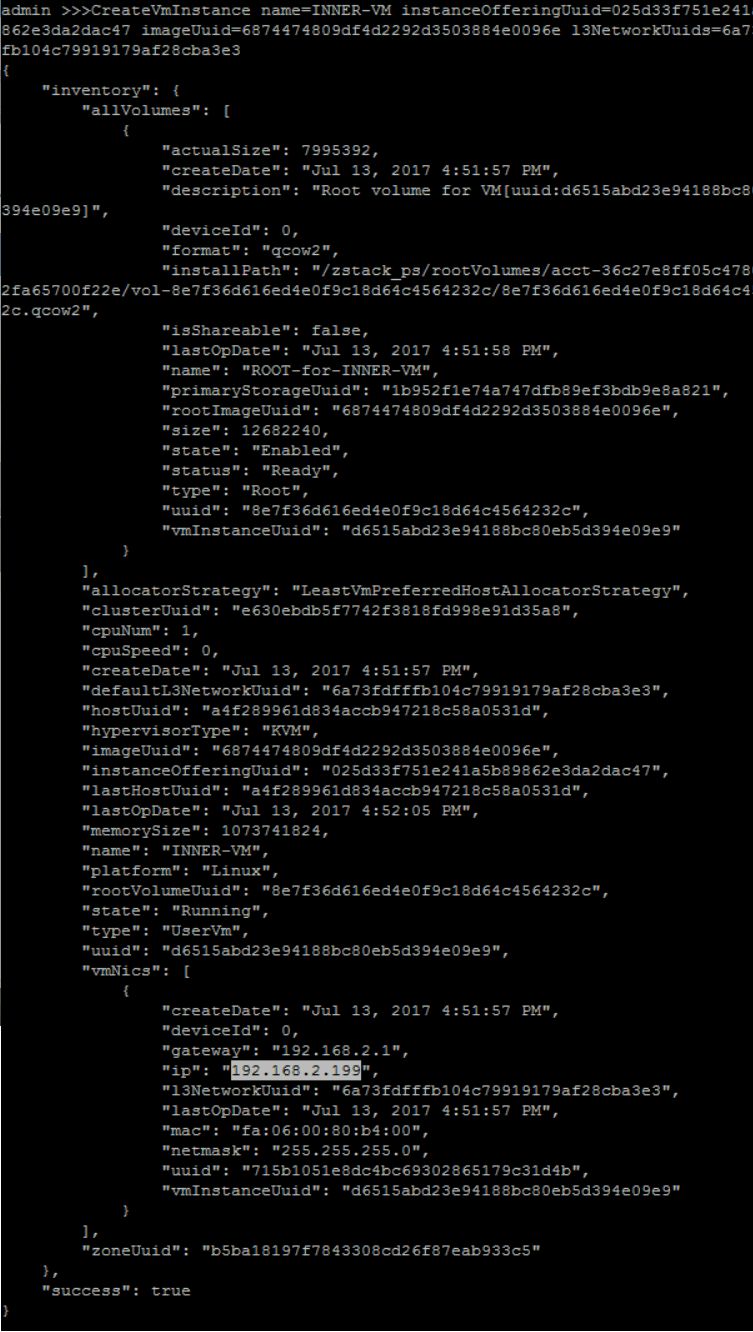
from VM creation result, you can get the new created VM IP address is 192.168.2.199
16. Join INNER-VM Into Security Group
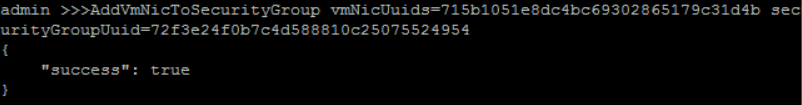
add 'INNER-VM' NIC to 'SECURITY-GROUP-1':
QuerySecurityGroup fields=uuid name=SECURITY-GROUP-1QueryVmNic fields=uuid vmInstance.name=INNER-VM>>> AddVmNicToSecurityGroup vmNicUuids=715b1051e8dc4bc69302865179c31d4b securityGroupUuid=72f3e24f0b7c4d588810c25075524954
17. Create OUTER-VM
create a new guest VM instance with instance offering 'small-instance', image 'zs-sample-image', L3 network 'PRIVATE-L3', name 'OUTER-VM' and hostname 'outer'
QueryInstanceOffering fields=uuid, name=small-instanceQueryImage fields=uuid, name=zs-sample-imageQueryL3Network fields=uuid, name=FLAT-L3>>> CreateVmInstance name=OUTER-VM instanceOfferingUuid=025d33f751e241a5b89862e3da2dac47 imageUuid=6874474809df4d2292d3503884e0096e l3NetworkUuids=6a73fdfffb104c79919179af28cba3e3
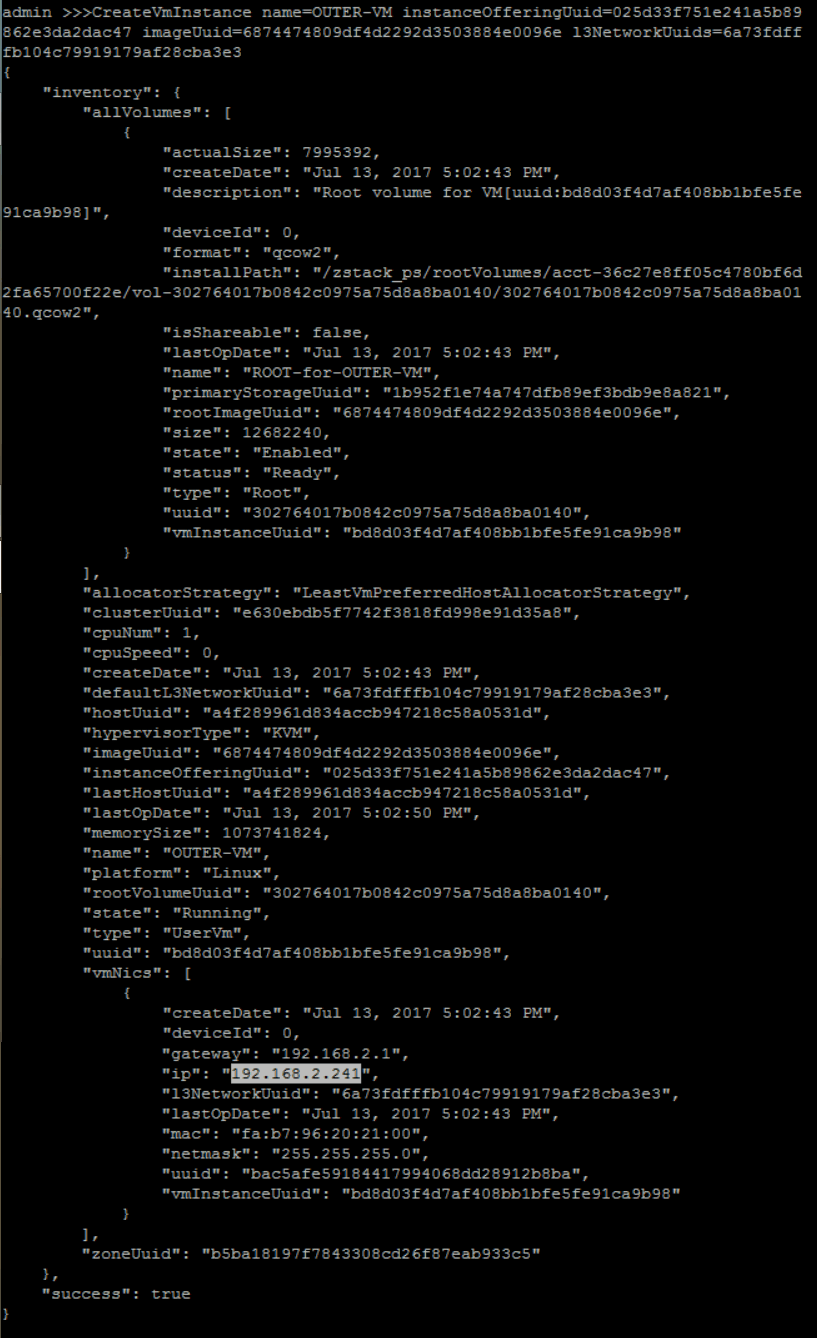
from VM creation result, you can get the new created VM IP address is 192.168.2.241
18. SSH Login INNER-VM From OUTER-VM
use a machine that can reach subnet 192.168.2.0/24 to SSH the OUTER-VM's IP '192.168.2.241'
QueryVmNic fields=ip vmInstance.name=OUTER-VM#ssh root@192.168.2.241
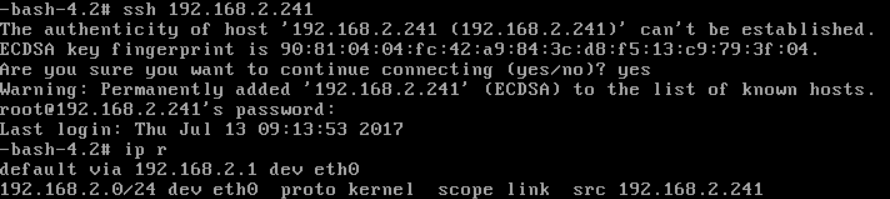
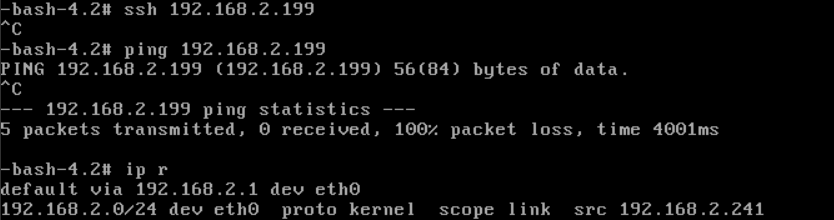
in OUTER-VM, ssh INNER-VM's IP '192.168.2.199', it should failed:
QueryVmNic fields=ip vmInstance.name=INNER-VM#ssh root@192.168.2.199
19. Delete Security Group Rule
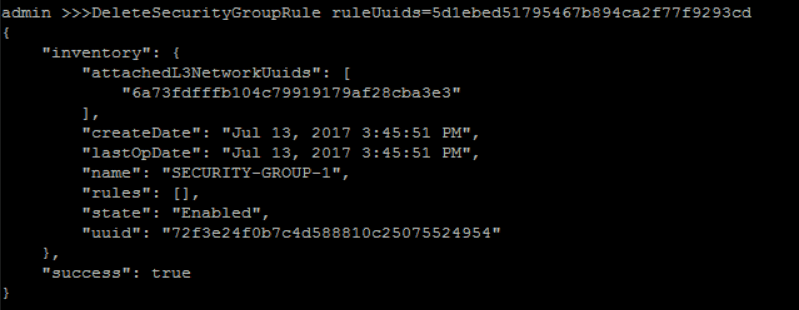
delete 'SECURITY-GROUP-1' rule:
QuerySecurityGroupRule fields=uuid startPort=22 endPort=22>>> DeleteSecurityGroupRule ruleUuids=5d1ebed51795467b894ca2f77f9293cd
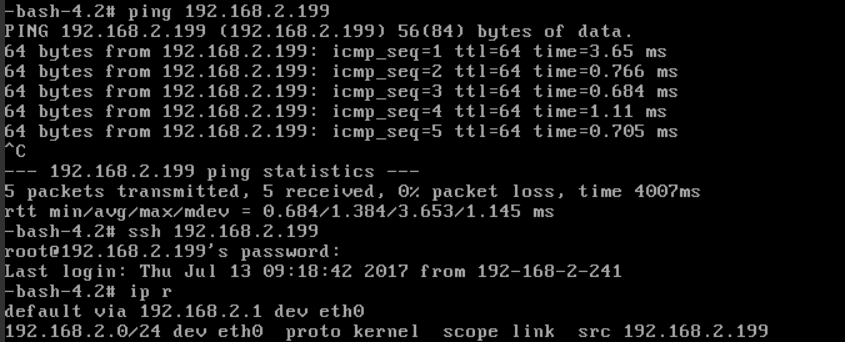
20. Confirm Unable to SSH Login INNER-VM From OUTER-VM
go back to OUTER-VM and ssh INNER-VM again, it should success.
Summary
In this tutorial, we showed you the basics of using security group. Though we only show one security group with one L3 network and one VM; you can actually create many security groups and attach them to different L3 networks; you can also put many VMs in the same security group. For more details, please visit Security Group in user manual.